The Consent Imperative
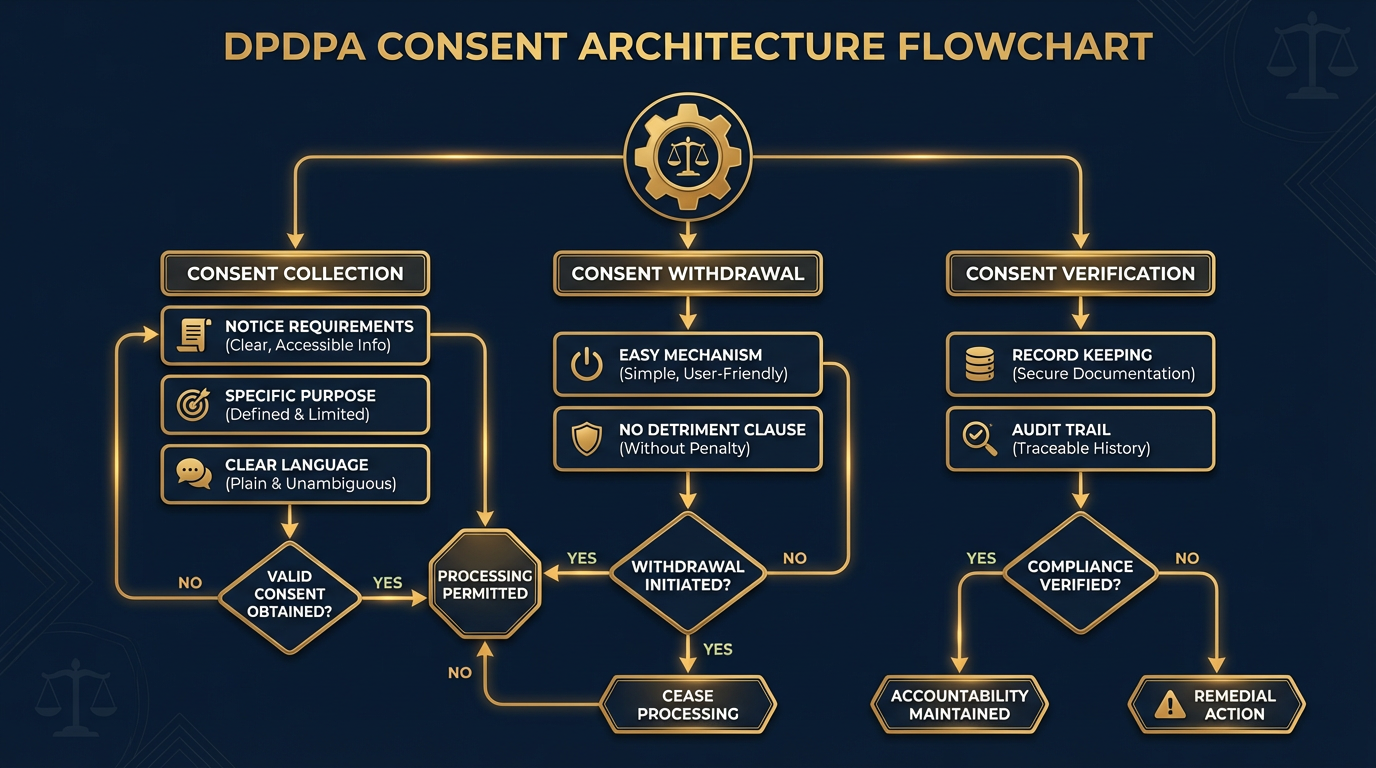
Section 6 of the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023 places consent at the heart of lawful data processing in India. The law requires consent to be free, specific, informed, unconditional, and unambiguous. This means organisations must obtain clear affirmative action from users before processing their data.
The legislation specifically bans pre ticked boxes and bundled consent mechanisms. Any consent obtained through deception or coercion is invalid. Data Fiduciaries need to present consent requests in clear, plain language that explains exactly why personal data will be processed.
This marks a significant shift from the old "deemed consent" approaches that were common in Indian data practices. Organisations now need to completely redesign how they interact with users and collect their consent.